- Skin
- Tranexamic Acid With Vitamin C
Can You Use Tranexamic Acid With Vitamin C?

Vitamin C is well-known in the world of skincare, health, wellbeing and beyond. Famously found in citrus fruits and some veggies too, this vitamin is also known as ascorbic acid and works, in the world of skincare, as an antioxidant that helps protect against pollution, environmental damage and even sun damage. This one's a key to a brighter, more luminous complexion.
As is tranexamic acid, the synthetic amino acid which, although not yet at the stardom status of Vitamin C, proves a promising up-and-comer. Gentle on the skin, yet tougher on dark spots, hyperpigmentation and inflammation, it's a melanin inhibitor, which makes it less likely for post-breakout and post-inflammatory marks to surface or linger.
Can You Use Tranexamic Acid With Vitamin C?
Yes—and this pairing can be a powerhouse for brightening your skin.
Tranexamic acid and vitamin C both target hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and uneven tone, but they do so through different mechanisms. Vitamin C brightens by boosting antioxidant protection and interfering with melanin production, while tranexamic acid interrupts the chemical signals that trigger excess pigment in the first place.
Used together, they can tackle discolouration from multiple angles, making them a great combination for those dealing with sun damage, melasma, or post-acne marks. Better still, they’re generally safe to layer—with low risk of irritation when applied with care.
If you're looking for a way to brighten your complexion, even out tone, and fade pigmentation without compromising skin health, this duo is well worth considering.
👉 Already know the benefits of each ingredient?
Jump To Routine
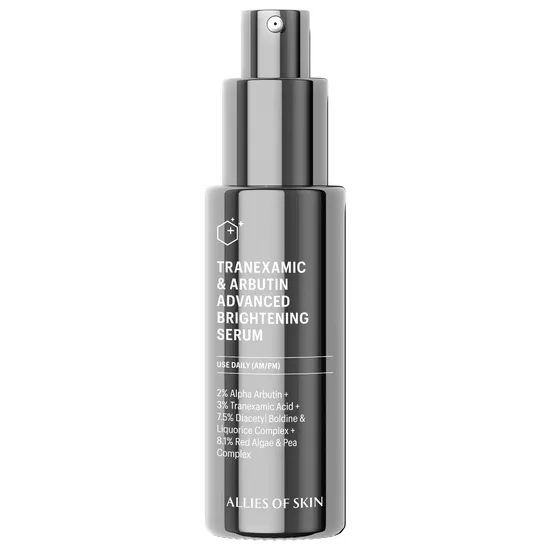
What does tranexamic acid do for the skin?
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. While it was originally used in medicine to reduce bleeding, it's gained popularity in skincare for its ability to lighten dark spots and treat stubborn pigmentation—particularly melasma and sun-induced damage.
It works by blocking the interaction between melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) and keratinocytes (skin cells), effectively reducing excess melanin production at the source.
Key benefits of tranexamic acid:
- Fades dark spots: Helps lighten hyperpigmentation and melasma
- Evens skin tone: Reduces blotchiness and discolouration
- Gentle brightening: Safe for all skin tones, including deeper complexions
- Soothes inflammation: Calms the skin and reduces flare-ups
- Supports barrier-friendly routines: Low irritation potential
Best for:
- Melasma and stubborn pigmentation
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
- Red, uneven, or blotchy skin tone
- Sensitive skin or compromised barriers
Tranexamic acid is typically used at 2–5% concentration in serums, toners, or creams and can be used once or twice daily depending on the product and your skin's tolerance.
What does vitamin C do for the skin?
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid and its derivatives) is one of the most popular and well-studied antioxidants in skincare. It helps protect the skin from environmental damage, brightens dull skin, fades hyperpigmentation, and boosts collagen production.
It also inhibits tyrosinase—an enzyme involved in melanin production—making it highly effective for fading sun spots and improving skin radiance over time.
Key benefits of vitamin C:
- Brightens and evens skin tone: Reduces pigmentation and dullness
- Fades dark spots: Inhibits melanin production
- Boosts collagen synthesis: Supports firmer, more youthful skin
- Protects against free radicals: Neutralises environmental damage
- Enhances sunscreen effectiveness: Pairs well with daily SPF use
Best for:
- Dull or tired-looking skin
- Sun damage and age spots
- Hyperpigmentation and post-acne marks
- Anyone building a morning antioxidant routine
Vitamin C can be used daily (typically in the morning) and comes in a variety of forms—including L-ascorbic acid, magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, and sodium ascorbyl phosphate—ranging from 5% to 20% concentration.
Can you use tranexamic acid and vitamin C together?
Yes—and using them together can significantly enhance brightening results.
There’s no evidence to suggest that tranexamic acid and vitamin C conflict or deactivate each other. On the contrary, they address pigmentation through complementary pathways—vitamin C as an antioxidant and pigment inhibitor, and tranexamic acid as a melanin signal interrupter.
This makes them especially effective for treating:
- Melasma
- Sun spots
- PIH (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation)
- Uneven tone and dullness
They're also both considered safe for daily use and suitable for a range of skin types, including sensitive and darker skin tones.
Why this combo works:
- Multi-pathway pigment reduction: Target melanin production from different angles
- Gentle and effective: Both ingredients are well tolerated when introduced gradually
- Boosts skin clarity and radiance: Vitamin C brightens, tranexamic evens tone
Antioxidant support + pigment control: Great for preventative and corrective routines
Comparing Tranexamic Acid With Vitamin C Side-by-Side
| Benefit | Tranexamic Acid | Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Targets dark spots and pigmentation by blocking melanin formation | Antioxidant that brightens and defends against free-radical damage |
| Fades Hyperpigmentation | ✅ Highly effective for melasma and post-inflammatory marks | ✅ Strong brightening and spot-fading effects |
| Brightens Dull Skin | ✅ Evens tone and restores radiance | ✅ Revives glow and enhances luminosity |
| Reduces Redness & Inflammation | ✅ Anti-inflammatory and calming | ⚠️ Can occasionally sting on sensitive skin |
| Boosts Collagen | ❌ Not a collagen stimulator | ✅ Promotes collagen synthesis for firmer skin |
| Antioxidant Protection | ⚠️ Minimal antioxidant benefit | ✅ Strong antioxidant defence |
| Hydration & Barrier Support | ✅ Helps maintain barrier strength and moisture balance | ⚠️ May cause dryness in higher concentrations |
| Suitable for Sensitive Skin | ✅ Generally very well tolerated | ⚠️ Use gentle or stabilised forms |
| Best Time to Use | AM or PM (pairs well with Vitamin C) | AM (for antioxidant protection) |
How to safely combine glycolic acid and vitamin C
✅ Option 1: Layer vitamin C first, then tranexamic acid (recommended)
Vitamin C is most effective when applied to freshly cleansed skin, followed by tranexamic acid.
Routine (AM):
- Cleanse skin
- Apply vitamin C serum (wait ~1 minute)
- Apply tranexamic acid serum
- Follow with moisturiser
- Finish with SPF
✅ Option 2: Use vitamin C in the morning, tranexamic acid at night
This method spreads the active ingredients across the day to reduce layering fatigue and minimise irritation risk.
- AM: Vitamin C → Moisturiser → SPF
- PM: Tranexamic acid → Moisturiser
This schedule is ideal for those with sensitive or reactive skin or anyone using other actives like retinoids at night.
A.M.
P.M.
✅ Option 3: Use a formula that combines both
Some brightening serums now include both tranexamic acid and vitamin C in a single formula, often alongside niacinamide or licorice root for additional pigment control.
If choosing this option, make sure the product is well-formulated (e.g., stabilised vitamin C, low-irritation base) and start slowly.

Written by Maria Mukaranda
Maria’s background is rooted primarily in creative media and a love for all things written, expressed through experience both online and in print; for creative platforms spanning from music to fashion to beauty.
Top Posts